home All News open_in_new Full Article
Artificial muscle flexes in multiple directions, offering a path to soft, wiggly robots

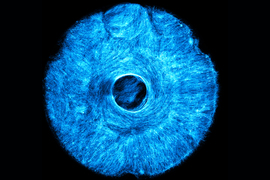
MIT engineers developed a new stamping method to grow artificial muscle tissue that flexes in multiple directions, mimicking natural muscle movement. This allows for the creation of biohybrid robots with enhanced range of motion. The artificial muscle structure, demonstrated with an iris-like design, pulls concentrically and radially. This approach can be used to grow complex patterns of muscle and other biological tissues for various applications, including neuromuscular injury restoration and soft robotics.
today 1 week ago attach_file Politics
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Events
attach_file
Economics
attach_file
Events
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Events
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Politics
attach_file
Economics
ID: 3754464195